RVM
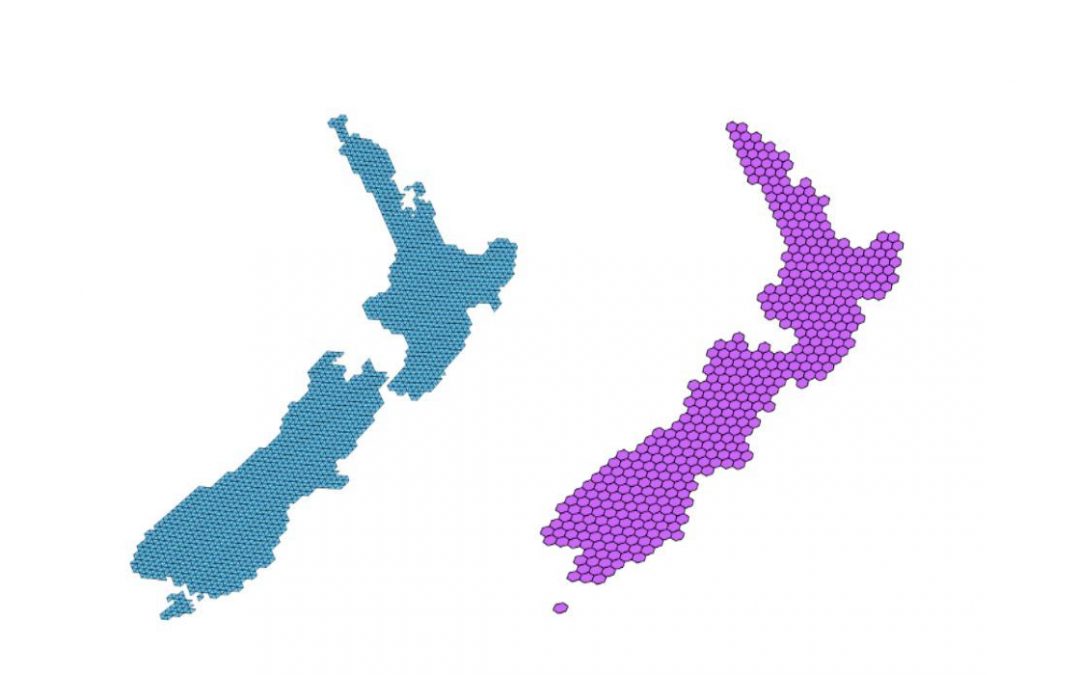
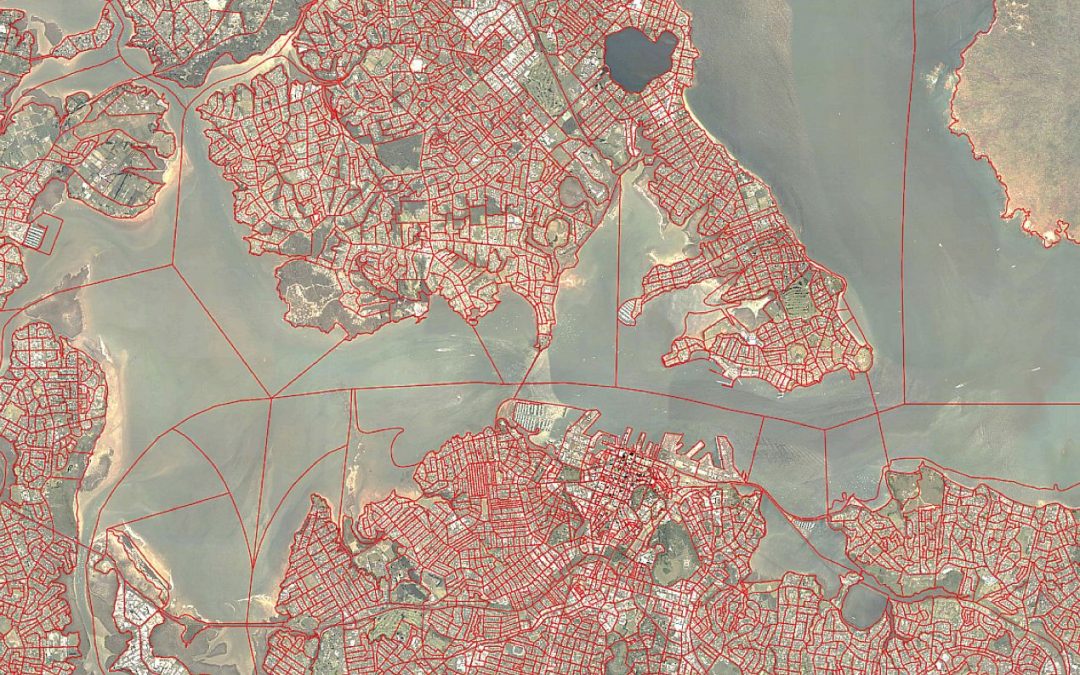
A geodesic discrete global grid is a partitioning of the surface of the globe into a grid of equal area cells. An indexed hierarchy of grids at multiple interrelated levels of resolution is called a discrete global grid system (DGGS).

RVM
Professor Richard Easther from Physics Department has been asking questions about the universe for more than 20 years. He’s uncovered just as many new questions as answers in that time. “The universe is continually making space between the galaxies,” says Easther. “The explosion that started our universe is still making space today.”
RVM
Dr Sharp is collaborating with William Newman, a Professor in Physics & Astronomy at UCLA, to investigate whether the Nice model, the leading model for the Solar System’s evolution, accurately predicts the present day orbits of the giant planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.

RVM
New Zealand’s next census will take place in March 2018. The census is an official count of all the people and dwellings in New Zealand, and will involve around two-and-a-half-thousand field officers and cover almost two million households.
RVM
There has been significant growth in interest around machine learning and its applications to research. This has largely been driven by advances in algorithms, particularly in neural networks where the use of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) has reduced the time to train complex or ‘deep’ neural networks by orders of magnitude. With the rise of ‘big data’, researchers are increasingly finding opportunities to apply these methods to deliver new insights.

RVM
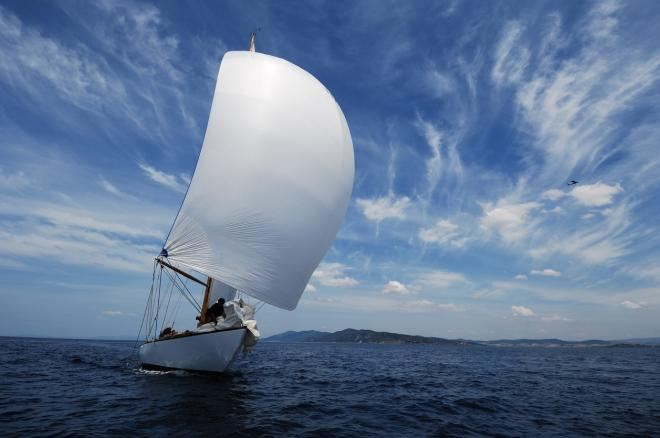
As any experienced seafarer knows, good aerodynamics is the key to smooth sailing. In order to improve the design of sails, hulls, and masts, we need to better understand the properties of sail aerodynamics in a range of conditions. At the University of Auckland, Stefano Nava, Stuart Norris and John Cater in the Faculty of Engineering are using NeSI computing resources to study the aerodynamics of high performance yachts.





