Multigene environmental DNA data analysis for New Zealand genomic observatory
Alexei Drummond, Dong Xie, Department of Computer Science, Andrew Dopheide, School of Biological Sciences, NZGO (Genomicobservatory ) team
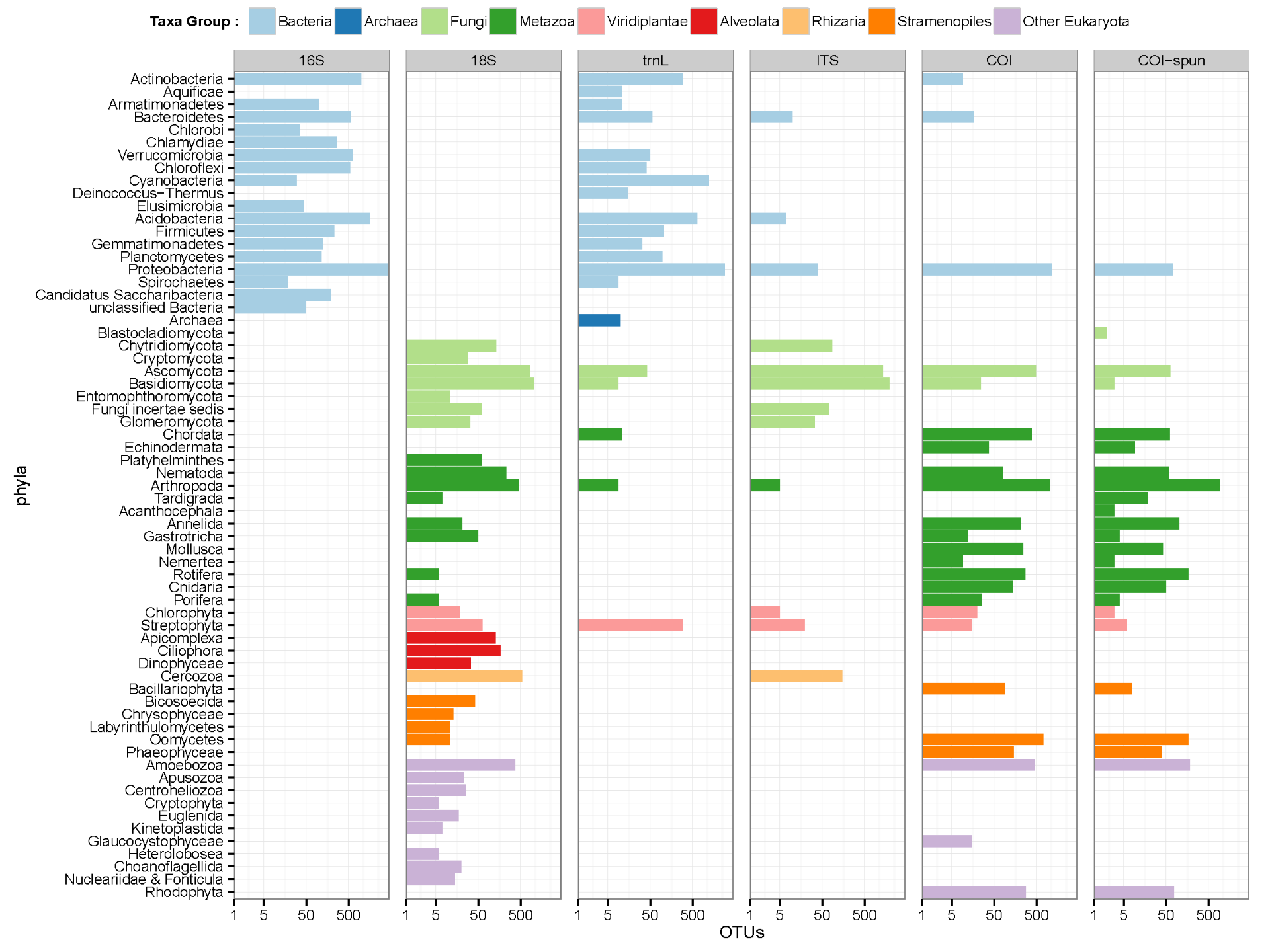
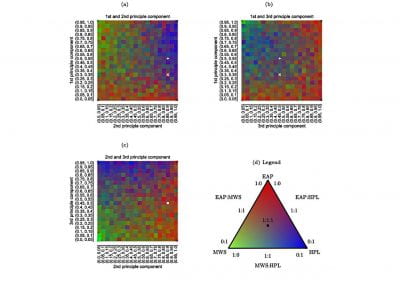
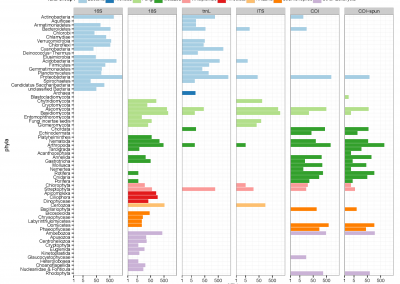
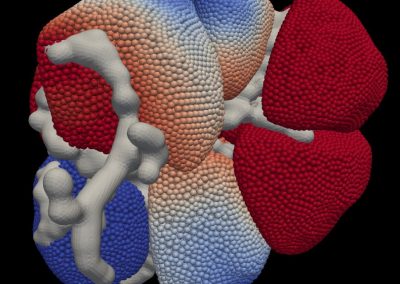
The percentage of OTUs at the 97% clustering threshold assigned to phyla. Unclassified OTUs, OTUs containing low-complexity sequences, and OTUs from phyla that are represented by less than 0.1% of the OTUs are grouped into the “Others’’ category.
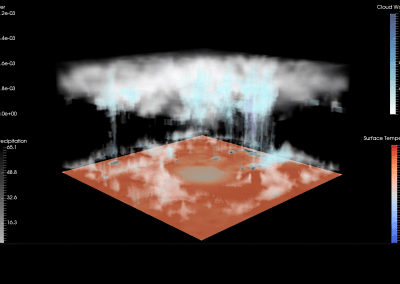
In the project, we are able to measure broad diversity of eukaryotes from soil using an environmental DNA approach. Environmental DNA (eDNA) approaches typically focus on microbial communities within the soil and tend to use single gene marker regions. Here we evaluate a suite of DNA markers coupled with Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) that span across the tree of life. Sequences analysis, such as Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) identification by molecular markers, taxonomic assignment, and biodiversities estimation, is a main part of this evaluation.
The raw reads file in a FASTQ format was then passed into a UPARSE pipeline (Edgar, 2013) to identify OTUs, which includes quality filtering, length truncation (300 bp), dereplication, abundance sorting, OTU clustering, chimera filtering and mapping OTUs. The outputs of the pipeline were a FASTA file containing OTU sequences and a mapping file between OTUs and reads for each given OTU clustering threshold. The community matrix was created from the mapping file by retrieving the site information added in the sequence label previously, and the matrix described species abundance (OTU counts) according to sampling sites.
Jost’s biodiversities (Jost 2006) are respectively calculated regarding community matrices of six eDNA methods using R package vegetarian (Charney and Record 2012). Rarefraction curves for diversities are further estimated using a 97% threshold for OTU identification by subsampling the minimum number of OTUs of sampling sites (subplots) using R ecology package vegan (Oksanen et al 2013). BLAST+ was used to classify the taxonomy of OTUs, and the classification result was interpreted to taxonomic assignment by phyla.
To learn more about the project, please refer to the project webpage www.genomicobservatory.cs.auckland.ac.nz and the database link https://data.genomicobservatory.cs.auckland.ac.nz.
See more case study projects

Our Voices: using innovative techniques to collect, analyse and amplify the lived experiences of young people in Aotearoa
Painting the brain: multiplexed tissue labelling of human brain tissue to facilitate discoveries in neuroanatomy

Detecting anomalous matches in professional sports: a novel approach using advanced anomaly detection techniques
Benefits of linking routine medical records to the GUiNZ longitudinal birth cohort: Childhood injury predictors
Using a virtual machine-based machine learning algorithm to obtain comprehensive behavioural information in an in vivo Alzheimer’s disease model
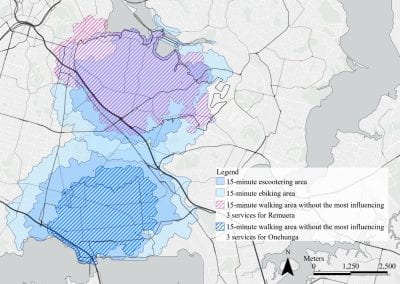
Mapping livability: the “15-minute city” concept for car-dependent districts in Auckland, New Zealand
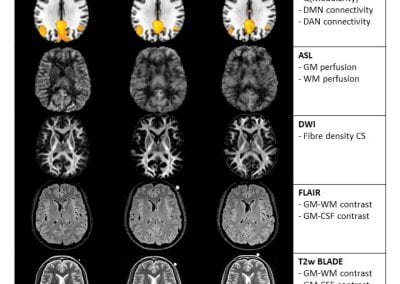
Travelling Heads – Measuring Reproducibility and Repeatability of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Dementia
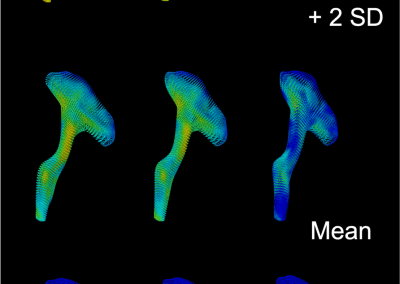
Novel Subject-Specific Method of Visualising Group Differences from Multiple DTI Metrics without Averaging

Re-assess urban spaces under COVID-19 impact: sensing Auckland social ‘hotspots’ with mobile location data
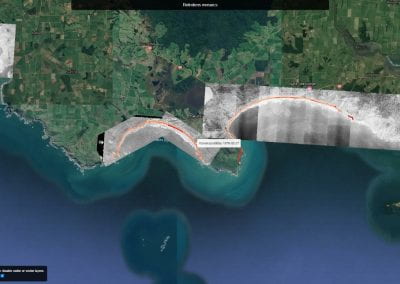
Aotearoa New Zealand’s changing coastline – Resilience to Nature’s Challenges (National Science Challenge)
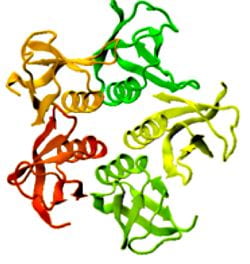
Proteins under a computational microscope: designing in-silico strategies to understand and develop molecular functionalities in Life Sciences and Engineering
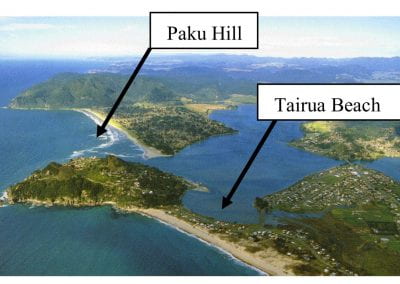
Coastal image classification and nalysis based on convolutional neural betworks and pattern recognition
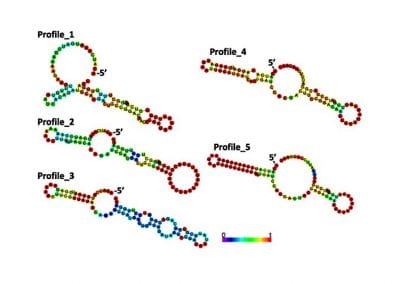
Determinants of translation efficiency in the evolutionarily-divergent protist Trichomonas vaginalis
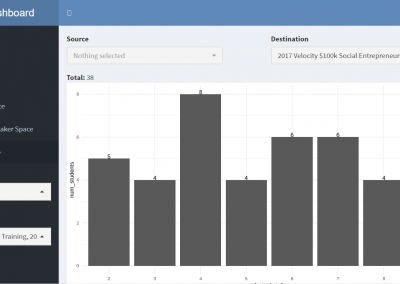
Measuring impact of entrepreneurship activities on students’ mindset, capabilities and entrepreneurial intentions

Using Zebra Finch data and deep learning classification to identify individual bird calls from audio recordings
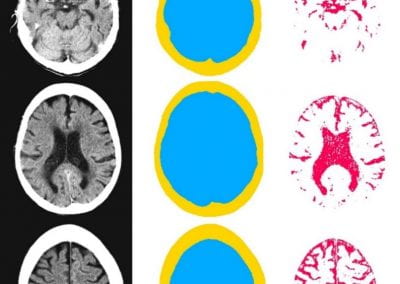
Automated measurement of intracranial cerebrospinal fluid volume and outcome after endovascular thrombectomy for ischemic stroke

Using simple models to explore complex dynamics: A case study of macomona liliana (wedge-shell) and nutrient variations
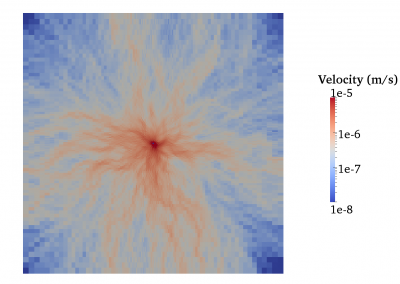
Fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical modelling of permeability enhancement by the finite element method

Modelling dual reflux pressure swing adsorption (DR-PSA) units for gas separation in natural gas processing
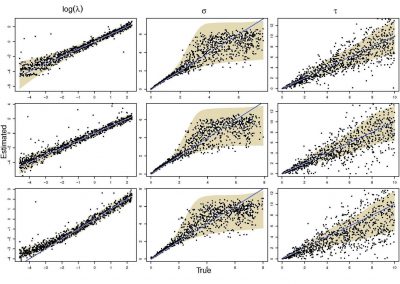
Molecular phylogenetics uses genetic data to reconstruct the evolutionary history of individuals, populations or species
Wandering around the molecular landscape: embracing virtual reality as a research showcasing outreach and teaching tool